Home > Immunology Assays > Macrophages/Monocytes
Assays for measuring monocyte and macrophage activation, cytokine release, migration, phagocytosis and polarisationMacrophages and monocytes are key effector cells of the innate immune system and are largely responsible for engulfing dying cells and pathogens. Macrophage dysregulation can be a key contributor to autoimmune, inflammatory and fibrotic diseases as well as cancer. Tissue resident macrophage populate organs early in development and may also be replenished by infiltrating monocytes which subsequently differentiate. Specialisedtissue resident macrophage populations include microglia in the brain and Kupffer cells in the liver.
Macrophages and monocytes display considerable heterogeneity, and whilst classically have been divided into ‘M1’ (‘pro-inflammatory’) and ‘M2’ (‘pro-resolution/anti-inflammatory’, ‘pro-fibrotic’) phenotypes, single cell studies have enabled identification of discrete phenotypes associated with function and/or location such as plaque associated macrophages, synovial tissue macrophages, tumour-associated macrophages, colitis-associated macrophages and scar-associated macrophages. Celentyx offers a range of established assays which support the development of therapeutics targeting macrophages. These range from comprehensive phenotyping studies performed using spectral flow cytometry and using a range of polarizing conditions (including those to study ‘M1’ and ‘M2’ phenotypes), to functional studies that quantify key macrophage functions such as phagocytosis and cytokine release. These studies can be performed using macrophages derived from human monocytes and also on cells isolated from human resected tissue. Assays may be suitable for evaluating modulators of ABCA7, adenosine receptors, Arginase, CD33, CD80, CD86, CD209, FcgRs, IDO, NLRP3, P2RX7, P2RY12, PI3K, TLRs, SIRPa, STAT3, STING, and others. Selected publication list... |
Further Immunology Assays
Antigen-specific Assays B Cells Fibroblasts Haemolysis Testing Human Microglia Neutrophils/Granulocytes NK Cells Phagocytosis Assays Regulatory T cells Spheroid Killing Assays Suppression Assays T Cell Activation Assays T Cell Exhaustion Assays TIL and dissociated tumour cell assays Tumour Cell Killing Assays |
|
Polarisation & phenotyping
Quantitative analysis of macrophage phenotype under polarising conditions (‘stimulus’) by flow cytometry (A) or imaging (B) enables the impact of therapeutics to be evaluated in a disease relevant context. Reduction in costimulatory molecules such as CD80 and CD86 may reduce antigen-presenting function, whereas changes in phagocytic or scavenger receptors such as CD206 or CD209 may indicate changes in phagocytic function.
|
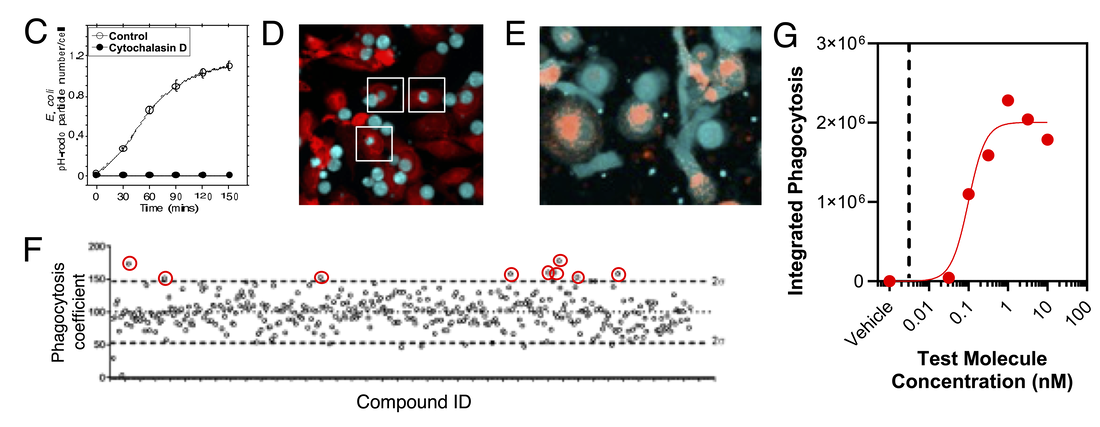
Phagocytosis assays
Testing the impact of molecules on phagocytosis of a range of cargos such as pH-rodo labelled E.coli (C), target cells (D) or labelled aggregated proteins (E) can be performed by high-content imaging in plate-based formats suitable for screening (F), with subsequent in-depth pharmacological characterisation (G) against a range of cargos. Also see our dedicated phagocytosis assays page.
Signaling
|
Measuring early signaling events in response to a pro-inflammatory stimulus often forms a key part of our offering for testing molecules early in a screening cascade. However, as these events are target proximal, they often can translate to biomarkers that can be used with patient samples. Assays with monocytes are often performed by flow cytometry (pseudo-colour plot, H, shows subdivision of monocyte subsets) or adherent macrophages by high-content imaging. Different subsets of monocytes or macrophages may exhibit varying sensitivities to stimuli and/or test molecules as shown by differential phosphorylation of a signaling molecule and inhibition by a reference molecule (I). Also see our dedicated phosphoflow page.
|
Cytokine Release
The release of cytokines is a major function of macrophages. The impact of test molecules on pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine release can be investigated in response to stimuli and/or phagocytosis (J). Cytokines are quantified by simple ELISA assays through to multiplex assays such as Luminex (K) which can simultaneously quantify multiple cytokine readouts.
Phenotyping of macrophages from patient tissue
Phenotyping of ‘myeloid’ populations isolated from patient tissues can validate target expression and be used to infer disease-relevant mechanisms. The right-hand pseudocolour plots (L) show identification of the indicated myeloid populations isolated from patient tissue macrophages/dendritic cells, and lower histograms (M) show expression of additional markers characterised on each of these subpopulations.
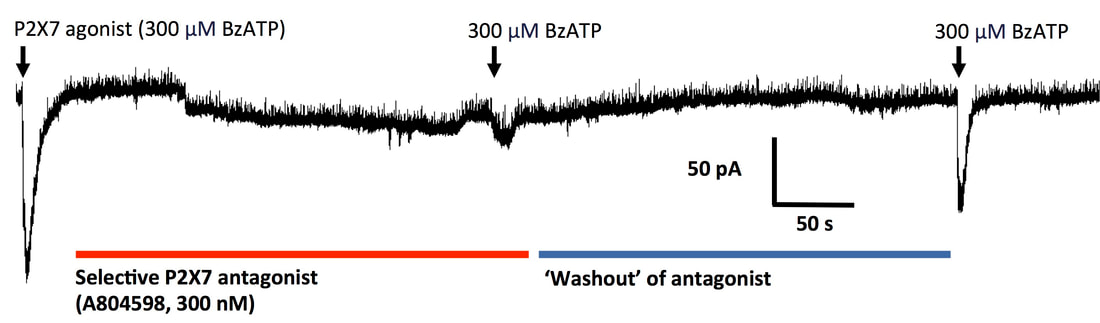
Electrophysiology - microglia - the macrophages of the brain
The brain contains specialised macrophage populations called microglia with important roles in maintaining homeostasis and in neuroinflammatory disease. The recording below shows inhibition of a P2X7 response by a P2X7 antagonist in a human microglial cell. Also see our dedicated microglia and neuroinflammation pages.