Autoimmunity and inflammation therapeutic development using human immune cellsCelentyx provide a range of assays to support the development of therapeutics for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Assays are typically performed with human immune cells purified from the blood of healthy volunteers or patients, or disease tissue from patients. Most cell types, including rare lymphocyte subsets, can be purified either via magnetic-bead based purification or by FACS, and cultures established in plate-based formats for testing of therapeutics and potential therapeutics. Typical readouts include multi-colour flow-cytometry or CyTof, ELISA, multiplex analysis of analytes via Luminex and high-content imaging. Celentyx have experience performing functional assays on a wide-range of immune cells and quantifying a wide-range of outputs. Some examples are shown below:
Also see dedicated T cell, suppression assays (regulatory T cells), B cell, monocyte/macrophage and phagocytosis pages.
Assays are also suitable for evaluating the impact of modulators of Arginase, CD28, CD39, CD55, CD73, CD80, CD86, CR1, CTLA-4, Fas, FasL, GITR, IDO, LAG-3, PD-1, PDL-1, PDL-2, PKC, PI3K TGFβ, TIGIT, TIM-3, TLRs and others, on the function of B cells, macrophages, monocytes, NK cells, T cell subsets.
1. Inhibition of IL-6-evoked phospho-STAT3 signaling in immune cell subsetsMultiparameter flow cytometry coupled with phospho-flow enables a target proximal readout to be evaluated in multiple immune cell subsets. The example below shows CD4 T cell responses in a PBMC stimulation, and inhibition by reference inhibitors.
|
2. B cell phenotyping and functional responses
B cells play a central role in various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, both through antibody production and through cytokine and antigen-presenting functions. Celentyx have optimised several culture systems for investigating the impact of therapeutics and potential therapeutics on B cell functions.
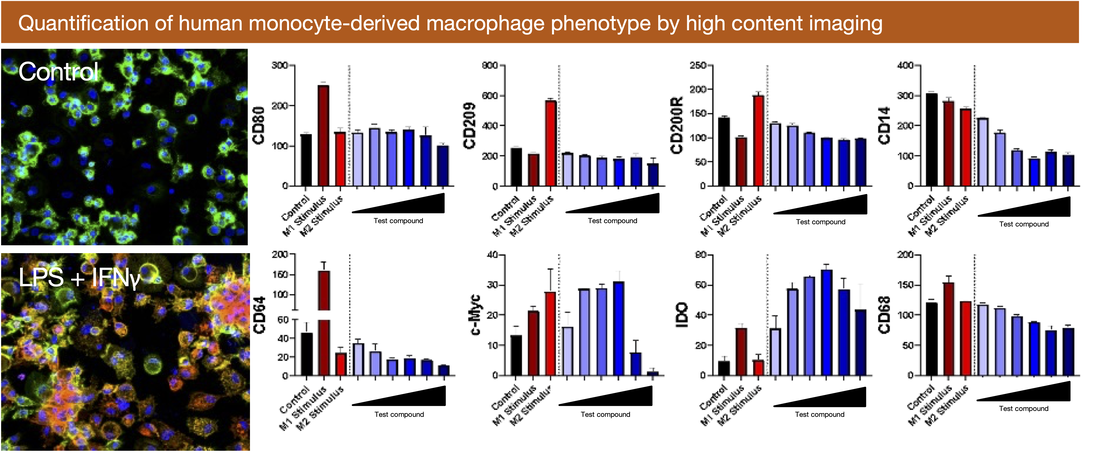
3. Macrophage differentiation and function
Macrophages play a central role in controlling tissue homeostasis and as a result, are key drivers in both inflammation and pathogenic tissue damage, and resolution of inflammation and tissue repair. Celentyx has developed a range of assays for interrogating macrophage function, which include quantitative high-content imaging assays enabling macrophage phenotype (for example ‘M1’ to ‘M2’ polarisation spectrum) and phagocytic ability to be quantified in their adherent state. Alternatively macrophages can be analysed by flow cytometry in suspension (using appropriate cell culture consumables) to enable detailed phenotyping of additional markers simultaneously.